Creating a Global Standard for Zero Emission Ports
Hydrogen-Powered Crane Development Project
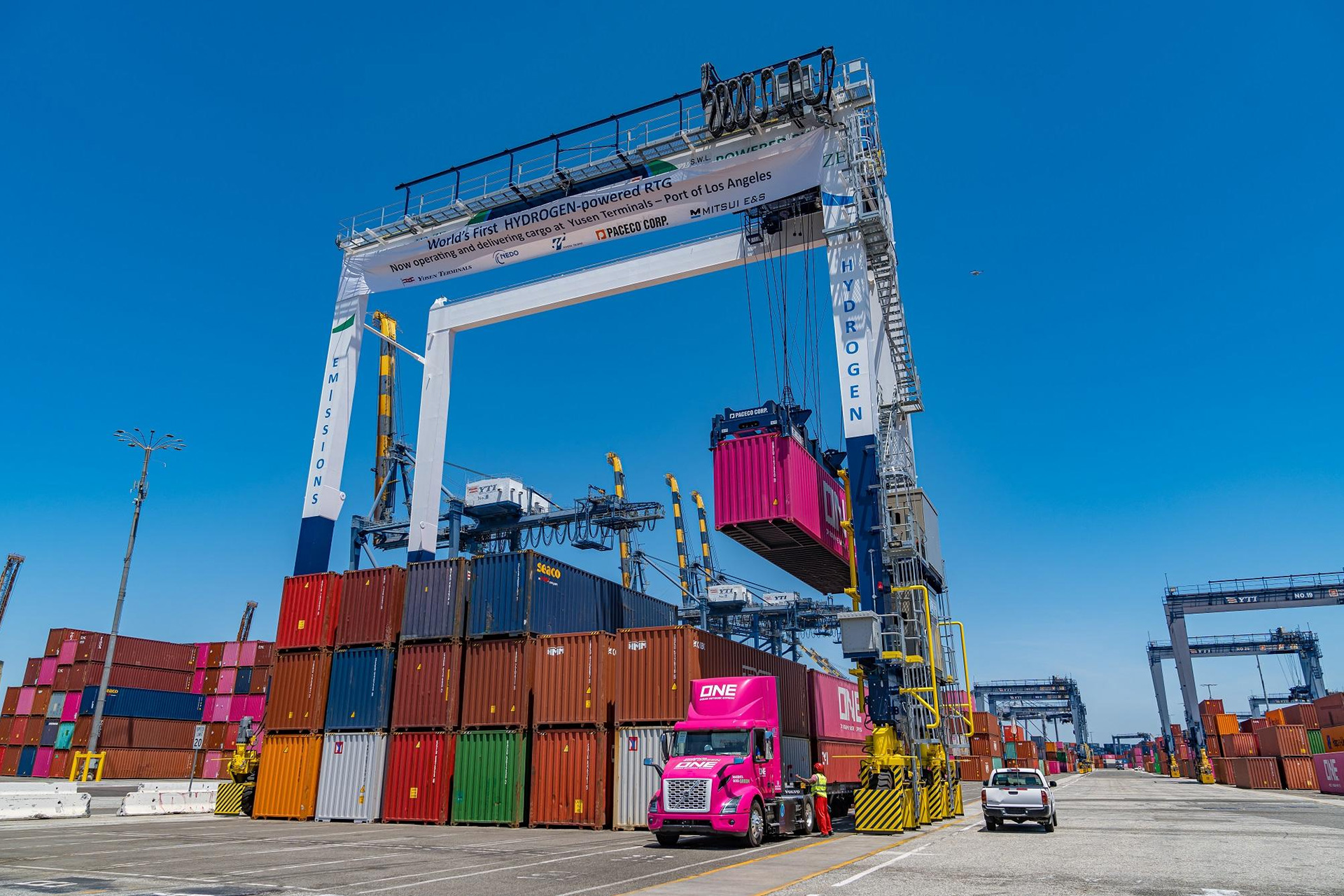

In May 2024, we, MITSUI E&S, and our U.S. subsidiary, PACECO Corp., commenced commercial operations of the world's first Rubber-Tyred Gantry crane (RTG) "MITSUI-PACECO H2-ZE TRANSTAINER CRANE (H2-ZE TRANSTAINER)" equipped with hydrogen fuel cells (FC) at the Port of Los Angeles. The Port Authorities of Los Angeles and Long Beach established the "Clean Air Action Plan (CAAP)" in 2006, aiming to eliminate diesel exhaust emissions from port areas by 2030. The MITSUI E&S Group continues to challenge this ambitious goal of achieving zero emissions (ZE) at ports.
MITSUI E&S's RTG Leading Environmental Initiatives
Ports, which are crucial hubs in the international supply chain and where over 99% of import and export cargo passes through, face urgent issues not only in terms of environmental considerations but also in forming competitive ports.
The Rubber-Tyred Gantry cranes (RTG) which are essential for container handling within container terminals are powered by electricity generated from diesel engine generators mounted on the cranes, and necessitate measures against air pollution caused by exhaust gases.
In the 2000s, MITSUI E&S has developed filters for diesel engines to remove particulate matter (PM) and nitrogen oxides (NOx). In 2009, we commenced sales of hybrid RTG that reduce fuel consumption and exhaust emissions by reusing regenerative electric power generated during cargo handling. As a pioneer in developing clean cargo handling equipment, we have delivered 330 units to domestic and international ports.
Since 2012, we have also been providing electrified RTG that receive necessary power from external sources. Additionally, we have developed and provide FC RTG that use hydrogen as fuel to enable the use of clean cargo handling equipment even at terminals where the installation of shore power supply facilities is challenging.
Environmental Initiatives for RTG

Since 2000
Development of diesel exhaust gas filters for RTG

2007
Delivery of the first capacitor hybrid RTG
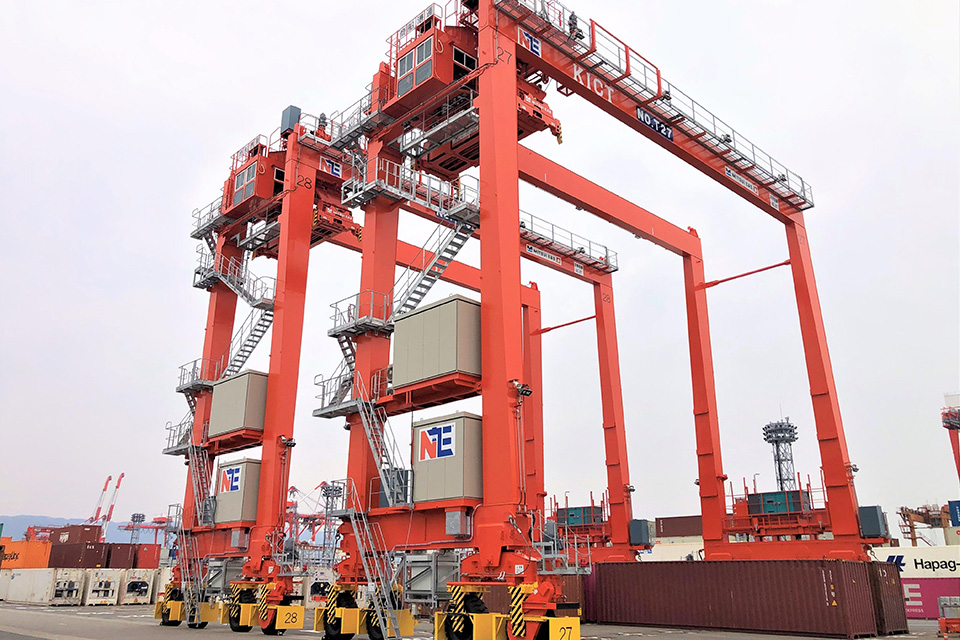

2011
Delivery of the first lithium-ion battery hybrid RTG
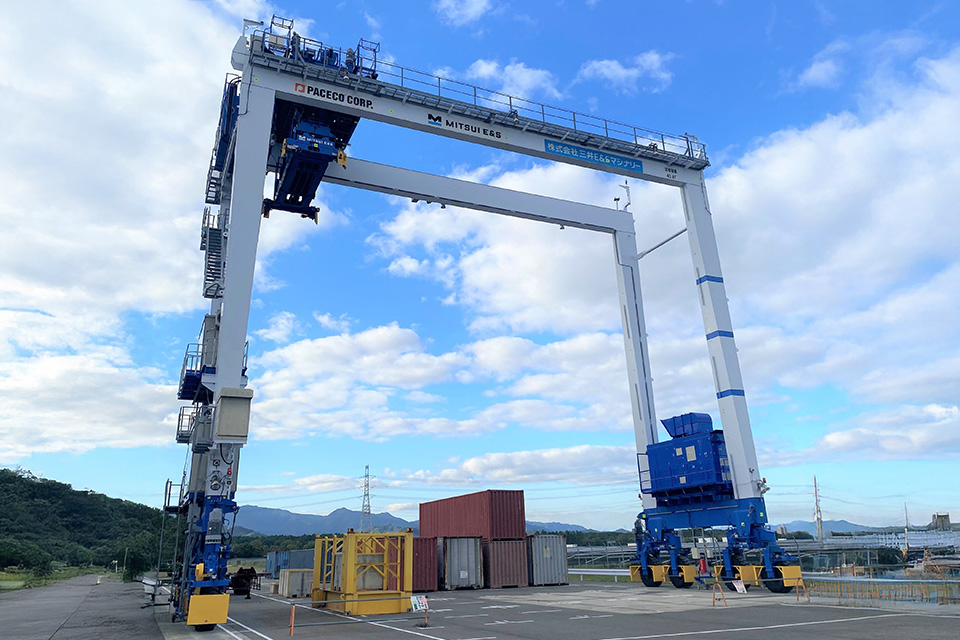

2019
Initiation of development for Near Zero Emission RTGC/Zero Emission RTG
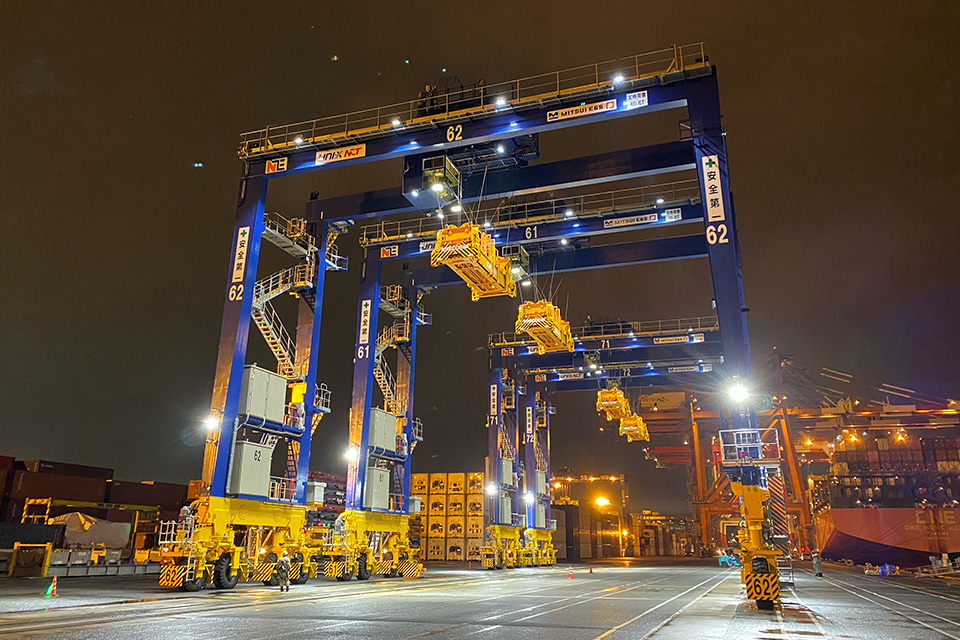

2022
Delivery of the first Near Zero Emission RTG unit

2024
Commercial cargo handling with the world's first FC-powered RTG
World's first RTG powerd by FC.
Beyond reducing exhaust emissions, we started developing FC-powered RTG since fiscal year 2021 with support from NEDO (New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization) to achieve zero emissions at ports. In May 2024, we commenced commercial cargo handling at the Port of Los Angeles, boasting stable operational performance.
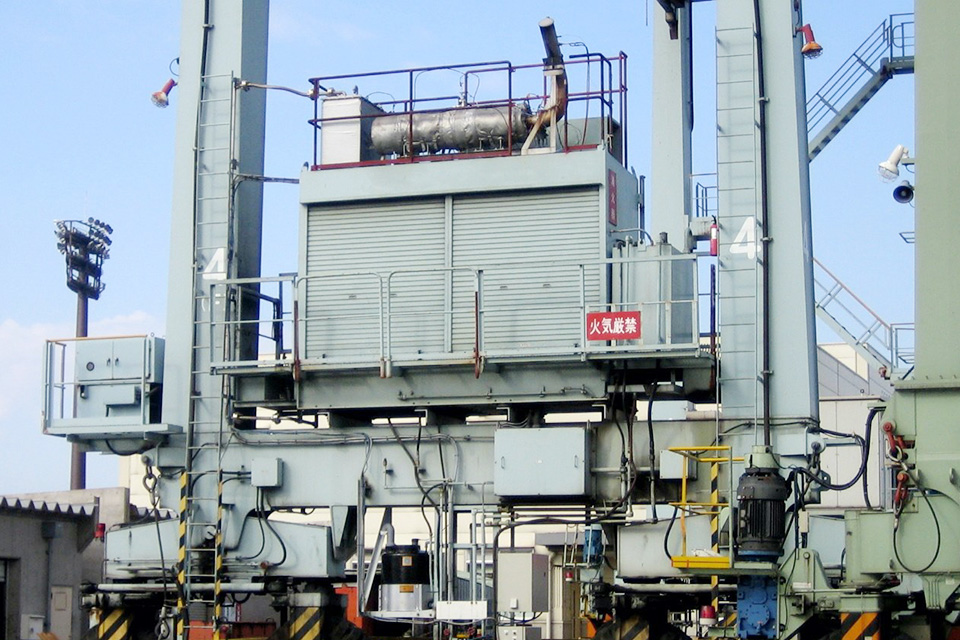
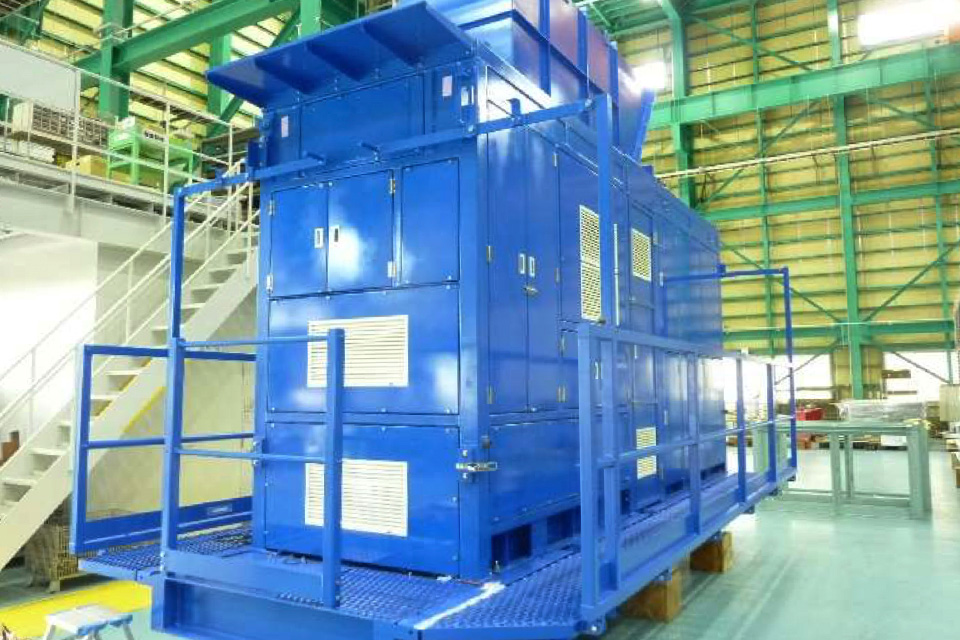
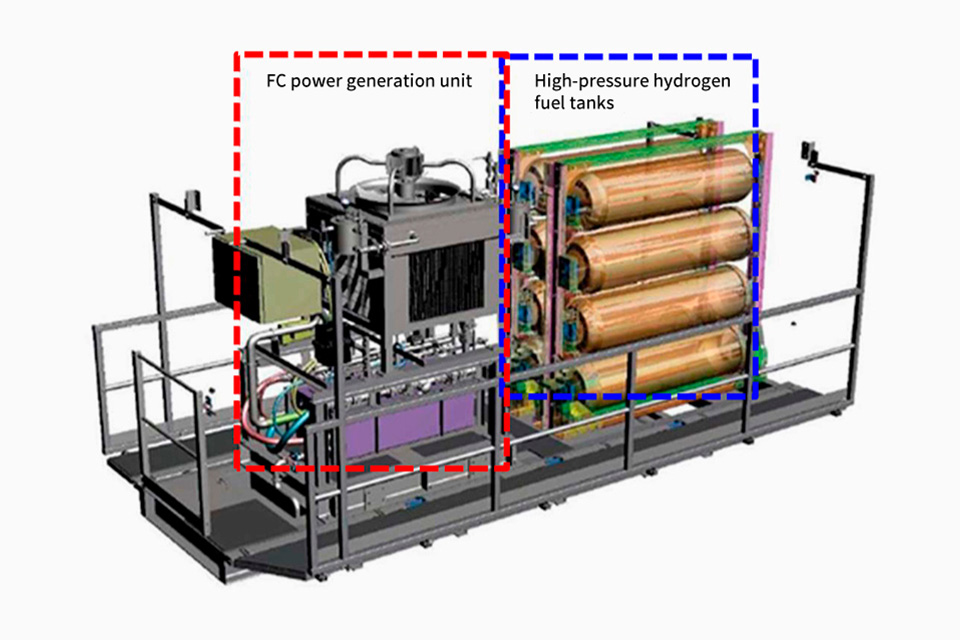
In April 2023, at Oita factory, we developed the world's first FC-powered "H2-ZE TRANSTAINER" with cargo handling capabilities equivalent to cranes equipped with conventional diesel engine generators. The hybrid RTG is composed of diesel engines generator set and lithium-ion batteries. By replacing the diesel engine generator set with an FC Power Pack consisting of FC and hydrogen tanks and increasing the capacity of the lithium-ion batteries, RTG can store all energy generated by the FC Power Pack in the large-capacity batteries and handle cargo using only the power supplied from the large-capacity batteries. This enables instantaneous output and realizes RTG that can operate continuously with FC.
*NEDO: New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization
RTG equipped with FC Power Pack
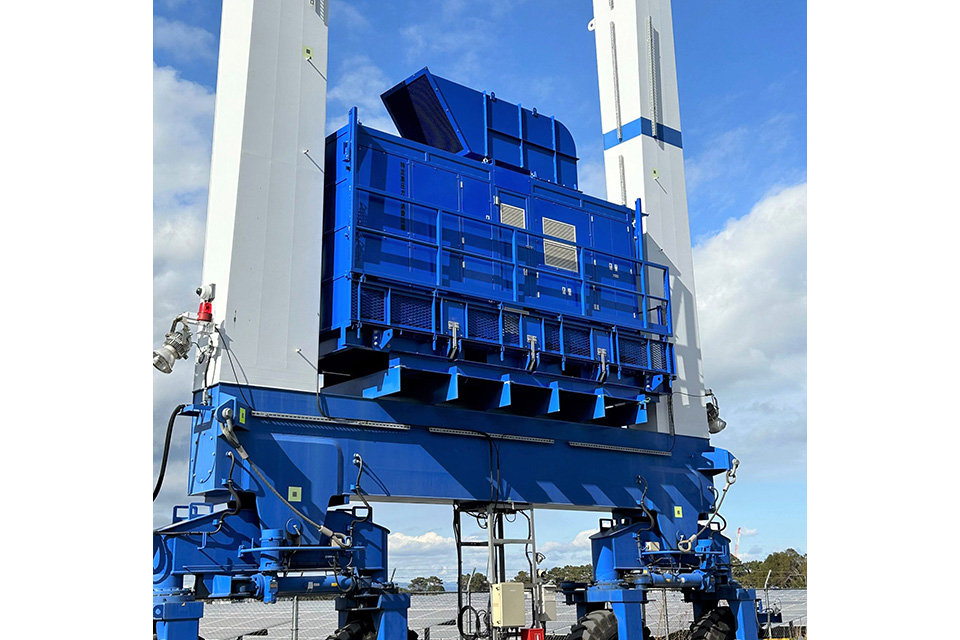


Equipment Configuration of FC Power Pack

Towards a New Standard for Zero Emission Ports
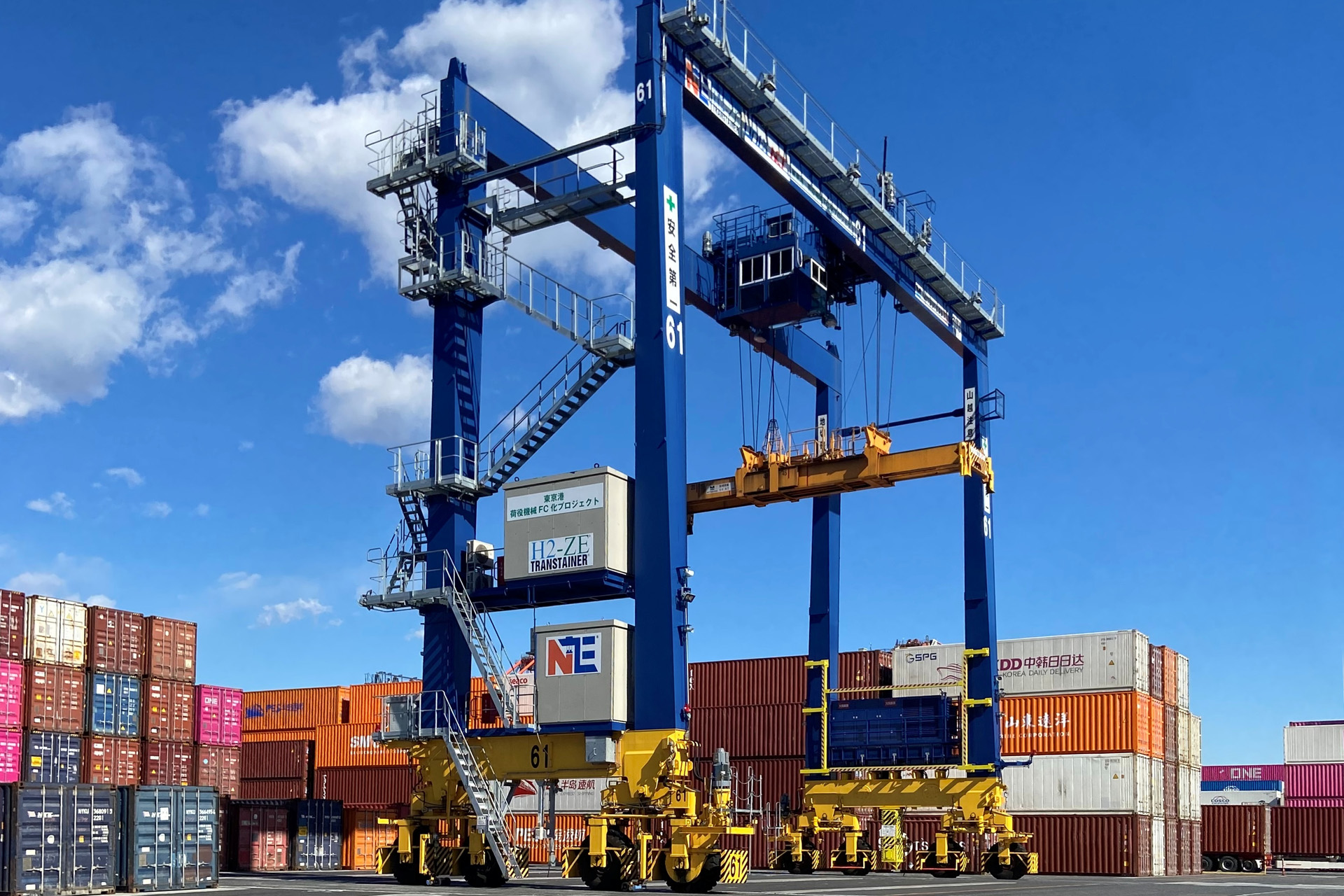
We are conducting operational demonstrations to convert RTG to hydrogen powered at Tokyo, Yokohama, and Kobe ports. In October 2024, we implemented FC Power Pack on RTG at the Oi Container Terminal and commenced cargo handling operations using RTG fueled by hydrogen for the first time in Japan. By replacing the diesel engine generator of the operating RTG with an FC Power Pack, we are verifying whether we can achieve cargo handling capabilities equivalent to those before the conversion while using hydrogen as fuel, which does not emit CO2 during power generation.
Commencement of Cargo Handling Operations Using Hydrogen-Fueled RTG for the First Time in Japan
Since May 2022, MITSUI E&S has been working with the Tokyo Metropolitan Government's Bureau of Port and Harbor, Nippon Yusen Kabushiki Kaisha, UNI-X NCT CORPORATION, and Iwatani Corporation to convert the diesel engine geneator set of near-zero emission RTG operating at the Oi Container Terminal to FC Power Packs and implement cargo handling operations using hydrogen as fuel.
In October 2024, we commenced cargo handling operations using RTG converted to FC powered RTG, achieving cargo handling capabilities equivalent to those before the conversion while using hydrogen as fuel, which does not emit CO2 during power generation.
The results of this project will be widely disseminated to promote the use of hydrogen in cargo handling machinery and contribute to the decarbonization of the Port of Tokyo.

